What are Plate Tectonics?
Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that describes the large-scale motions of Earth's lithosphere. The lithosphere is divided into several tectonic plates that move and interact with each other. This theory explains the formation of mountains, earthquakes, volcanoes, and the distribution of geological features on the Earth's surface.
Key Concepts and Processes
1. Tectonic Plates
The Earth's lithosphere is divided into several large and small tectonic plates, which are in constant motion. The movement of these plates is driven by processes occurring in the Earth's mantle.
2. Plate Boundaries
Plate boundaries are the areas where tectonic plates interact. There are three main types of plate boundaries:
- Divergent Boundaries: Where two tectonic plates move away from each other, leading to the formation of new crust. This process is known as seafloor spreading.
- Convergent Boundaries: Where two plates move towards each other, resulting in the subduction of one plate beneath the other, or the collision of two continental plates. This can lead to the formation of mountain ranges and deep ocean trenches.
- Transform Boundaries: Where two plates slide past each other horizontally, causing earthquakes along the boundaries.
3. Geological Features
Plate tectonics is responsible for the formation of various geological features, including mountains, volcanoes, and ocean basins. For example, the formation of the Himalayas is the result of the collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate.
Impact on Earth's Surface
Plate tectonics has a significant impact on the Earth's surface and its inhabitants. It influences the distribution of continents and oceans, the occurrence of natural disasters such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and the shaping of landscapes over geological time scales.
Study Guide
When studying plate tectonics, it's important to understand the following key points:
- The composition and structure of the Earth's lithosphere
- The movement and interactions of tectonic plates
- The types of plate boundaries and the geological features associated with each
- The impact of plate tectonics on the Earth's surface and natural processes
- The historical development of the theory of plate tectonics and the evidence that supports it
Be sure to review diagrams and maps showing the distribution of tectonic plates, as well as examples of geological features associated with different types of plate boundaries.
Understanding plate tectonics is crucial for comprehending the dynamic processes that shape the Earth's surface and its geological history.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson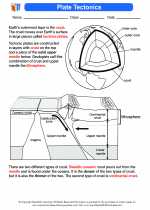
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
