Work and Machines
Work and machines are important concepts in the field of science and engineering. Understanding how work is done and how machines help us perform work is essential for understanding various aspects of the physical world.
What is Work?
In science, work is defined as the application of a force over a distance. When a force is applied to an object and the object moves in the direction of the force, work is being done. The formula for calculating work is:
Work (W) = Force (F) × Distance (d) × cos(θ)
Where θ is the angle between the force and the direction of motion.
Types of Machines
Machines are devices that help us perform work. There are several types of machines, including:
- Simple Machines: These are basic mechanical devices that do not require power, such as levers, pulleys, and inclined planes.
- Compound Machines: These are machines that are made up of two or more simple machines working together, such as a bicycle or a pair of scissors.
- Complex Machines: These are machines that are powered by engines or motors, such as cars, airplanes, and industrial machinery.
Mechanical Advantage
The mechanical advantage of a machine is a measure of how much a machine multiplies force or distance. It is calculated using the formula:
Mechanical Advantage (MA) = Output Force / Input Force
A machine with a mechanical advantage greater than 1 multiplies the input force, while a machine with a mechanical advantage less than 1 multiplies the input distance.
Study Guide
- Define work and explain the formula for calculating work.
- List and describe the three types of machines.
- Calculate the mechanical advantage of a machine given the input and output forces.
- Explain how machines make work easier and more efficient.
- Identify examples of simple, compound, and complex machines in everyday life.
Understanding the concepts of work and machines is crucial for understanding the principles of physics and engineering. By studying these concepts, you will gain a deeper understanding of how the physical world works and how machines help us accomplish tasks more efficiently.
[Work And Machines.] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Third Grade. Work and Machines.

 Study Guide
Study Guide
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson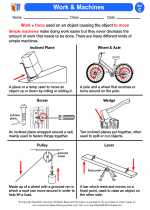
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
