What is Electricity?
Electricity is the flow of electric charge. This charge can be positive or negative, and it is carried by tiny particles called electrons. The movement of these electrons creates an electric current, which can be used to power various devices and systems.
Types of Electricity
There are two main types of electricity: static and current. Static electricity is the buildup of electric charge on the surface of an object, while current electricity is the flow of electric charge through a conductor.
Electric Circuits
An electric circuit is a path that allows electric current to flow. It typically consists of a power source (such as a battery or generator), conductive wires, and a load (such as a light bulb or motor). Circuits can be either series, where the components are connected end-to-end, or parallel, where the components are connected across common points.
Conductors and Insulators
Conductors are materials that allow electric charge to flow easily, while insulators are materials that resist the flow of electric charge. Metals such as copper and aluminum are good conductors, while materials like rubber and plastic are insulators.
Basic Electrical Components
There are several basic components in electrical circuits, including resistors, capacitors, inductors, and diodes. These components control the flow of electric current and are fundamental to the operation of various electronic devices.
Electric Safety
It's important to be aware of electrical safety when working with electricity. This includes using insulated tools, avoiding water near electrical devices, and following proper procedures for handling and connecting electrical components.
Applications of Electricity
Electricity is used in a wide range of applications, including lighting, heating, communication, transportation, and countless electronic devices. Understanding the principles of electricity is essential for modern technological advancements.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Sixth Grade. Electricity

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson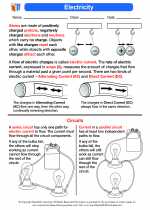
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
