Weather
Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions at a specific place and time. It includes elements such as temperature, humidity, precipitation, wind speed and direction, and atmospheric pressure. Weather is the result of complex interactions between the atmosphere, the sun, the earth's surface, and bodies of water.
Key Concepts
- Temperature: The measure of how hot or cold the air is. It is usually measured in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit.
- Humidity: The amount of moisture in the air. High humidity can make the air feel sticky, while low humidity can make the air feel dry.
- Precipitation: Any form of water, such as rain, snow, sleet, or hail, that falls from the atmosphere to the earth's surface.
- Wind: The movement of air from high pressure to low pressure areas. Wind speed and direction are important factors in weather forecasts.
- Atmospheric Pressure: The force exerted by the weight of the air above a given point on the earth's surface. It is an important factor in determining weather patterns.
Weather Tools
Scientists use various tools to measure and predict the weather. Some of these tools include:
- Thermometer: Used to measure temperature.
- Hygrometer: Used to measure humidity.
- Rain Gauge: Used to measure the amount of precipitation.
- Anemometer: Used to measure wind speed and direction.
- Barometer: Used to measure atmospheric pressure.
Weather Patterns
Weather patterns are the result of the interactions between the atmosphere, the earth's surface, and the sun. These patterns can include short-term changes, such as daily or weekly weather variations, as well as long-term changes, such as seasonal or climate changes.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember when studying weather:
- What are the key elements of weather?
- How do temperature and humidity affect the way we perceive the weather?
- What are the different forms of precipitation, and how are they formed?
- What causes wind, and how is it measured?
- Why is atmospheric pressure an important factor in weather forecasting?
- What tools do scientists use to measure and predict the weather?
- How do weather patterns form, and what are some examples of short-term and long-term weather patterns?
Understanding the concepts and patterns of weather can help us better prepare for and adapt to the changing conditions in our environment.
[Weather] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Weather

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson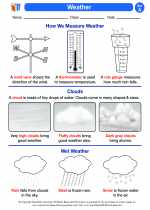
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
