Food Webs and Food Chains
Food webs and food chains are important concepts in ecology that help us understand the interactions between different organisms in an ecosystem. Let's dive into the details of these concepts!
Food Chains
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms, each of which serves as a source of food or energy for the next member in the sequence. It represents the flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another.
Here's an example of a simple food chain:
- Grass (producer)
- Grasshopper (primary consumer)
- Frog (secondary consumer)
- Snake (tertiary consumer)
In this food chain, energy and nutrients flow from the grass to the snake, with each organism serving as a food source for the next.
Food Webs
A food web is a more complex representation of the feeding relationships within an ecosystem. It consists of multiple interconnected food chains and shows the complex network of interactions between different organisms.
For example, a food web in a pond ecosystem may include interactions between various producers (such as algae and plants), herbivores (such as snails and insects), carnivores (such as frogs and fish), and decomposers (such as bacteria and fungi).
Study Guide
To understand food webs and food chains, it's important to remember the following key points:
- Identify the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers in an ecosystem.
- Understand the flow of energy and nutrients through a food chain.
- Recognize the interconnected nature of organisms in a food web.
- Explain how changes in one part of a food web can affect other organisms in the ecosystem.
By mastering these concepts, you'll gain a deeper understanding of how living organisms depend on each other for survival and how disruptions in food webs can have far-reaching impacts on ecosystems.
[Food Webs And Food Chains] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food Webs and Food Chains

 Study Guide
Study Guide
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson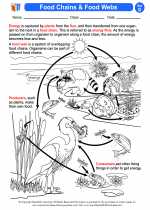
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
