Cell Processes
Cell processes are the series of events that occur within a cell to maintain its functions and carry out essential activities. These processes are fundamental for the survival and proper functioning of organisms. They include cellular respiration, photosynthesis, cell division, and protein synthesis, among others.
1. Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose and other organic molecules to produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The three main stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain.
Study Guide:
- What is cellular respiration?
- List the three main stages of cellular respiration.
- What is the primary purpose of cellular respiration?
2. Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose and other organic compounds. It occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells and involves two main stages - the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle.
Study Guide:
- Define photosynthesis.
- Where does photosynthesis take place in plant cells?
- What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
3. Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. This process is essential for growth, repair, and reproduction in multicellular organisms. The two main types of cell division are mitosis and meiosis.
Study Guide:
- What is cell division?
- What are the two main types of cell division?
- What is the primary purpose of mitosis?
- What is the primary purpose of meiosis?
4. Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells build proteins using the information encoded in DNA. It involves two main stages - transcription, where a complementary RNA molecule is synthesized from a DNA template, and translation, where the RNA molecule is used to assemble the corresponding protein at the ribosomes.
Study Guide:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Cell Processes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson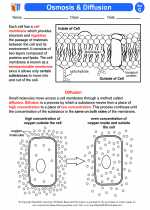
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
